Demographics of the United States
The United States has a total resident population of 311,359,000.[1] It is a very urbanized population, with 81% residing in cities and suburbs as of mid-2005 (the worldwide urban rate was 49%).[2] California and Texas are the most populous states,[3] as the mean center of United States population has consistently shifted westward and southward.[4]
The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2009 is 2.05 children per woman,[5] which is slightly lower than the replacement level of 2.1.[6] However, U.S. population growth is among the highest in industrialized countries,[7] since the vast majority of these have below-replacement fertility rates and the U.S. has higher levels of immigration.[5][8] The United States Census Bureau shows population increases ranging between 0.85% and 0.89% for the twelve-month periods ending in 2009.[9] Nonetheless, though high by industrialized country standards, this is below the world average annual rate of 1.19%.[7]
People under 20 years of age made up over a quarter of the U.S. population (27.6%), and people age 65 and over made up one-eighth (12.6%) in 2007.[10] The national median age was 36.7 years.[10] Racially, the U.S. has a White American majority. Minorities compose just over one-third of the population (102.5 million in 2007), with Hispanic and Latino Americans and African Americans as the largest minority groups, by ethnicity and race, respectively.[11]
The American population more than tripled during the 20th century—a growth rate of about 1.3% a year—from about 76 million in 1900 to 281 million in 2000. It reached the 200 million mark in 1967, and the 300 million mark on October 17, 2006.[12][13] Currently, population growth is fastest among minorities as a whole, and according to the Census Bureau's estimation for 2005, 45% of American children under the age of 5 belonged to minority groups.[14]
Hispanic and Latino Americans accounted for almost half (1.4 million) of the national population growth of 2.9 million between July 1, 2005, and July 1, 2006.[15] Immigrants and their U.S.-born descendants are expected to provide most of the U.S. population gains in the decades ahead.[16]
The Census Bureau projects a U.S. population of 439 million in 2050, which is a 46% increase from 2007 (301.3 million).[17] However, the United Nations projects a U.S. population of 402 million in 2050, an increase of 32% from 2007 (the UN projects a gain of 38% for the world at large).[18] In either case, such growth is unlike most European countries, especially Germany, Russia, Italy, and Greece, or Asian countries such as Japan or South Korea, whose populations are slowly declining, and whose fertility rates are below replacement.
As of 14 February 2011, the United States has 4.51% of the world's population.
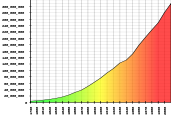 The first U.S. census, in 1790, recorded four million Americans. By 2000, this number had grown to 281 million. It is expected to reach 310 million by 2010 and 439 million[17] by 2050. |
 U.S. population clock hits the 300 million mark |
 United States population pyramid. |
| Historical populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 3,929,214 |
|
|
| 1800 | 5,236,631 | 33.3% | |
| 1810 | 7,239,881 | 38.3% | |
| 1820 | 9,638,453 | 33.1% | |
| 1830 | 12,866,020 | 33.5% | |
| 1840 | 17,069,453 | 32.7% | |
| 1850 | 23,191,876 | 35.9% | |
| 1860 | 31,443,321 | 35.6% | |
| 1870 | 38,558,371 | 22.6% | |
| 1880 | 49,371,340 | 28.0% | |
| 1890 | 62,979,766 | 27.6% | |
| 1900 | 76,212,168 | 21.0% | |
| 1910 | 92,228,496 | 21.0% | |
| 1920 | 106,021,537 | 15.0% | |
| 1930 | 123,202,624 | 16.2% | |
| 1940 | 132,164,569 | 7.3% | |
| 1950 | 151,325,798 | 14.5% | |
| 1960 | 179,323,175 | 18.5% | |
| 1970 | 203,211,926 | 13.3% | |
| 1980 | 226,545,805 | 11.5% | |
| 1990 | 248,709,873 | 9.8% | |
| 2000 | 281,421,906 | 13.2% | |
| 2010 | 309,162,581 | 9.9% | |
Contents |
History
Since the liberalization of immigration policy in 1965,[19] the number of first-generation immigrants living in the United States has quadrupled,[20] from 9.6 million in 1970 to about 38 million in 2007.[21] Almost 97% of residents of the 10 largest American cities in 1900 were non-Hispanic whites.[22] In 2006, non-Hispanic whites were the minority in thirty-five of the fifty largest cities.[23] The Census Bureau reported that minorities accounted for 48.6% of the children born in the U.S. between July 2008 and July 2009.[24]
Cities
The United States has dozens of major cities, including 8 of the 60 "global cities"[25] of all types, with three in the "alpha" group of global cities: New York City, Los Angeles and Chicago.[26][27] As of 2008[update], the United States had 52 metropolitan areas with a population of over 1,000,000 people each. (See Table of United States Metropolitan Statistical Areas.)
The following table shows the populations of the top ten cities and their metropolitan areas, as of July 1, 2008.
| Leading population centers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Core city | State | Pop.[28] | Metro area rank | Metro area pop.[29] | Region[30] |  New York City  Los Angeles |
| 1 | New York | New York | 8,363,710 | 1 | 19,006,798 | Northeast | |
| 2 | Los Angeles | California | 3,833,995 | 2 | 12,872,808 | West | |
| 3 | Chicago | Illinois | 2,853,114 | 3 | 9,569,624 | Midwest | |
| 4 | Houston | Texas | 2,242,193 | 6 | 5,728,143 | South | |
| 5 | Phoenix | Arizona | 1,567,924 | 12 | 4,281,899 | West | |
| 6 | Philadelphia | Pennsylvania | 1,447,395 | 5 | 5,838,471 | Northeast | |
| 7 | San Antonio | Texas | 1,351,305 | 28 | 2,031,445 | South | |
| 8 | Dallas | Texas | 1,279,910 | 4 | 6,300,006 | South | |
| 9 | San Diego | California | 1,279,329 | 17 | 3,001,072 | West | |
| 10 | San Jose | California | 948,279 | 31 | 1,819,198 | West | |
| 2008 U.S. Census Bureau estimates | |||||||
Population density
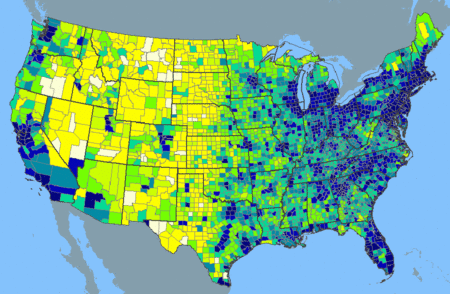
Population density for selected U.S. census-designated places (CDPs)
| Place | Government type | Density | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Friendship Village, Maryland | 31,657/km2 | 81,992/mi2 | |
| Manhattan, New York | Borough & County | 25,850/km2 | 66,940/mi2 |
| Guttenberg, New Jersey | Town | 21,961/km2 | 56,012/mi2 |
| Union City, New Jersey | City | 20,454/km2 | 52,978/mi2 |
| West New York, New Jersey | Town | 17,124/km2 | 44,352/mi2 |
| Edgewater, Illinois | 13,800/km2 | 35,743/mi2 | |
| Brooklyn, New York | Borough & County | 13,481/km2 | 34,917/mi2 |
| The Bronx, New York | Borough & County | 12,242/km2 | 31,709/mi2 |
| Hoboken, New Jersey | City | 11,675/km2 | 30,239/mi2 |
| Back Bay/Beacon Hill, Massachusetts | 11,463/km2 | 29,690/mi2 | |
| New York City, New York | City | 10,194/km2 | 26,403/mi2 |
| Maywood, California | City | 9,189/km2 | 23,887/mi2 |
| Cliffside Park, New Jersey | Borough | 9,253/km2 | 23,848/mi2 |
| East Newark, New Jersey | Borough | 9,178/km2 | 23,330/mi2 |
| Passaic, New Jersey | City | 8,425/km2 | 21,805/mi2 |
| Cudahy, California | City | 8,345/km2 | 21,628/mi2 |
| Great Neck Plaza, New York | Village | 8,052/km2 | 20,853/mi2 |
| Irvington, New Jersey | City | 7,926/km2 | 20,528/mi2 |
| Queens, New York | Borough & County | 7,880/km2 | 20,409/mi2 |
| North Bay Village, Florida | City | 7,825/km2 | 20,267/mi2 |
| Huntington Park, California | City | 7,819.5/km2 | 20,254/mi2 |
| Kaser, New York | Village | 7,468/km2 | 19,343/mi2 |
| West Hollywood, California | City | 7,335/km2 | 18,993/mi2 |
| Somerville, Massachusetts | City | 7,285/km2 | 18,868/mi2[31] |
| East Orange, New Jersey | City | 6,860/km2 | 17,777/mi2 |
| Bell Gardens, California | City | 6,842/km2 | 17,721/mi2 |
| Paterson, New Jersey | City | 6,826/km2 | 17,675/mi2 |
| Sweetwater, Florida | City | 6,774/km2 | 17,440/mi2 |
| San Francisco, California | City & County | 6,349/km2 | 16,443/mi2 |
| Long Beach, New York | City | 6,398/km2 | 16,595/mi2 |
| Jersey City, New Jersey | 6,195/km2 | 16,094/mi2 | |
| Chelsea, Massachusetts | City | 6,211/km2 | 16,086/mi2 |
| Lawndale, California | City | 6,192/km2 | 16,037/mi2 |
| Weehawken, New Jersey | Township | 6,136/km2 | 15,891/mi2 |
| South Floral Park, New York | Village | 6,091/km2 | 15,776/mi2 |
| Cambridge, Massachusetts | City | 6,086/km2 | 15,766/mi2 |
| Mount Vernon, New York | City | 6058/km2 | 15,689/mi2 |
| Central Falls, Rhode Island | 6,096/km2 | 15,652/mi2[32] | |
| Fairview, New Jersey | Borough | 6,021/km2 | 15,586/mi2 |
| Hawaiian Gardens, California | City | 5,942/km2 | 15,390/mi2 |
| Stone Park, Illinois | Village | 5,999/km2 | 15,378/mi2 |
| Hempstead, New York | Village | 5,547/km2 | 15,366/mi2 |
| Sunny Isles Beach, Florida | City | 5,881/km2 | 15,231/mi2 |
| Orange, New Jersey | Township | 5,754/km2 | 14,904/mi2 |
| Bell, California | City | 5,715/km2 | 14,803/mi2 |
| Cicero, Illinois | 5,651/km2 | 14,645/mi2 | |
| Lynwood, California | City | 5,556/km2 | 14,389/mi2 |
| Palisades Park, New Jersey | Borough | 5,449/km2 | 14,112/mi2 |
| Fort Lee, New Jersey | Borough | 5,412/km2 | 14,002/mi2 |
| Garfield, New Jersey | City | 5,399/km2 | 13,976/mi2 |
| Hawthorne, California | City | 5,359/km2 | 13,879/mi2 |
| Berwyn, Illinois | City | 5,361/km2 | 13,876/mi2 |
| Bay Harbor Islands, Florida | Town | 5,357/km2 | 13,875/mi2 |
| Millbourne, Pennsylvania | Borough | 5,309/km2 | 13,749/mi2 |
| Daly City, California | City | 5,353/km2 | 13,704/mi2 |
| Elmwood Park, Illinois | Village | 5,136/km2 | 13,328/mi2 |
| South Gate, California | City | 5,052/km2 | 13,084/mi2 |
| Manorhaven, New York | Village | 5,041/km2 | 13,056/mi2 |
| Hudson County, New Jersey | County | 5,036/km2 | 13,044/mi2 |
| Mount Rainier, Maryland | City | 5,034/km2 | 13,039/mi2 |
| Hermosa Beach, California | City | 5,013/km2 | 12,982/mi2 |
| Woodlynne, New Jersey | Borough | 4,996/km2 | 12,939/mi2 |
| Island Park, New York | Village | 4,938/km2 | 12,866/mi2 |
| New Square, New York | Village | 4,947/km2 | 12,812/mi2 |
| Chicago, Illinois | 4,866/km2 | 12,603/mi2 | |
| Miami Beach, Florida | 4,830/km2 | 12,502/mi2 | |
| Santa Ana, California | 4,751/km2 | 12,306/mi2 | |
| Boston, Massachusetts | 4,697/km2 | 12,166/mi2 | |
| Spring Valley, New York | 4,682/km2 | 12,123/mi2 | |
| Hialeah, Florida | 4,544/km2 | 11,768/mi2 | |
| Hamtramck, Michigan | 4,537/km2 | 11,750/mi2 | |
| Newark, New Jersey | 4,459/km2 | 11,548/mi2 | |
| Miami, Florida | 4,407/km2 | 11,534/mi2 | |
| Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | 4,190/km2 | 10,852/mi2 | |
| Yonkers, New York | 4,162/km2 | 10,780/mi2 | |
| Lakewood, Ohio | 3,895/km2 | 10,088/mi2 | |
| Berkeley, California | 3,793/km2 | 9,823/mi2[33] | |
| Washington, District of Columbia | 3,502/km2 | 9,070/mi2 | |
| Staten Island, New York | Borough & County | 3,246.3/km2 | 8,408/mi2 |
| Los Angeles, California | 3,078/km2 | 7,972/mi2 | |
| Baltimore, Maryland | 2,970/km2 | 7,693/mi2 | |
| Buffalo, New York | 2,786/km2 | 7,217/mi2 | |
| Oakland, California | 2,724/km2 | 7,054/mi2 | |
| Minneapolis, Minnesota | 2,691/km2 | 6,969/mi2 | |
| Seattle, Washington | 2,563/km2 | 6,639/mi2 | |
| New Haven, Connecticut | 2,527/km2 | 6,554/mi2 | |
| Detroit, Michigan | 2,470/km2 | 6,398/mi2 | |
| Milwaukee, Wisconsin | 2,399.5/km2 | 6,214.7/mi2 | |
| Cleveland, Ohio | 2,353/km2 | 6,095/mi2 | |
| St. Louis, Missouri | 2,199/km2 | 5,696/mi2 | |
| University City, Missouri | 2,457/km2 | 6,363.1/mi2 | |
| Mechanicville, New York | 2,091/km2 | 5,577/mi2 | |
| San Jose, California | 1,953/km2 | 5,059/mi2 | |
| Cincinnati, Ohio | 1,612/km2 | 4,174/mi2 | |
| Portland, Oregon | 1,503/km2 | 3,894/mi2 | |
| Atlanta, Georgia | 1,551.5/km2 | 4018.4/mi2 | |
| Denver, Colorado | 1,396.4/km2 | 3,642/mi2 | |
| Dallas, Texas | 1,348/km2 | 3,492/mi2 | |
| Columbus, Ohio | 1,307/km2 | 3,384/mi2 | |
| Houston, Texas | 1,287/km2 | 3,333/mi2 | |
| Phoenix, Arizona | 1,061/km2 | 2,749/mi2 | |
The most densely populated state is New Jersey (1,121/mi2 or 433/km2). See List of U.S. states by population density for maps and complete statistics.
The United States Census Bureau publishes a popular "dot" map showing population distribution at a resolution of 7,500 people,[34] as well as complete listings of population density by place name.[35]
Race and ethnicity
The U.S. population's distribution by race and ethnicity in 2008 was as follows:[36][37]
- Total population: 304.1 million
| Race and Hispanic or Latino origin | Percentage | Number |
|---|---|---|
| White alone (Not including the 29.2 million White Hispanic and Latino Americans: 65.4% or 198.9 million) |
75.0% | 228.2 million |
| Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, of any race | 15.4% | 46.9 million |
| Black or African American alone | 12.4% | 37.6 million |
| Some other race alone | 4.9% | 15.0 million |
| Asian alone | 4.4% | 13.4 million |
| Two or more races | 2.3% | 7.0 million |
| American Indian or Alaska Native alone | 0.8% | 2.4 million |
| Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander alone | 0.14% | 0.43 million |
These figures add up to more than 100% on this table because Hispanic and Latino Americans are distributed among all the races and are also listed as an ethnicity category, resulting in a double count.
Hispanic and Latino Americans
Each of the racial categories includes people who identify their ethnicity as Hispanic or Latino.[38] U.S. federal law defines Hispanic or Latino as "those who classify themselves in one of the specific Hispanic or Latino categories listed on the Census 2000 or ACS questionnaire - "Mexican", "Puerto Rican", or "Cuban" - as well as those who indicate that they are "other Spanish, Hispanic, or Latino.""[39] The total population of Hispanic and Latino Americans comprised 46.9 million or 15.4% of the national total in 2008, with the following racial distribution:[37]
- White alone: 62.4% or 29.2 million
- Some other race alone: 30.5% or 14.3 million
- Two or more races: 3.9% or 1.8 million
- Black or African American alone: 1.9% or 0.885 million
- American Indian or Alaska Native alone: 1.0% or 0.450 million
- Asian alone: 0.37% or 0.174 million
- Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander alone: 0.05% or 0.025 million
Projections
| 2008 | 2050 | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Hispanic whites | 66% | 46% |
| Hispanics (of any race) | 15% | 30% |
| African Americans | 14% | 15% |
| Asian Americans | 5% | 9% |
A report in August 2008[40] from the U.S. Census Bureau projects that non-Hispanic whites will no longer make up the majority of the population by 2042, but will remain the largest race. This is a revision of earlier projections that this would occur in 2050. Today, non-Hispanic White Americans make up about 66% of the population. This percentage is expected to fall to 46% in 2050. The report foresees the Hispanic and Latino population rising from 15% today to 30% by 2050. Today, African Americans make up 14% of the population, in 2050 they are projected to comprise 15%. Asian Americans make up 5% of the population and are expected to make up 9% in 2050. The U.S. has 308 million people today, and is projected to reach 400 million by 2039 and 439 million in 2050.[17][41][42]
A report from the Pew Research Center in 2008 projects that by 2050, non-Hispanic Whites will make up 47% of the population, down from 67% projected in 2005.[43] Non-Hispanic whites made up 85% of the population in 1960.[44] It foresees the Hispanic population rising from 14% in 2005 to 29% by 2050.[45] The proportion of Asian Americans would almost double by 2050. Overall, the population of the U.S. was due to rise from 296 million in 2005 to 438 million, with 82% of the increase due to immigration.[46]
Of the nation's children in 2050, 62% are expected to be of a minority ethnicity, up from 44% today. Approximately 39% are projected to be Hispanic (up from 22% in 2008), and 38% are projected to be single-race, non-Hispanic whites (down from 56% in 2008).[47]
Other subgroups
According to 2004 figures from the Census Bureau, there were some 32 million disabled adults (aged 18 or over) in the United States, plus another 5 million children and youth (under age 18).
There were 22.1 million veterans in 2009.[48]
In 2010, there were an estimated 11 million illegal immigrants in the country.[49]
The 2000 U.S. Census counted same-sex couples in an oblique way; asking the sex and the relationship to the "main householder", whose sex was also asked. One organization specializing in analyzing gay demographic data reported, based on this count in the 2000 census and in the 2000 supplementary survey, that same-sex couples comprised between 0.99% and 1.13% of U.S. couples in 2000.[50] A 2006 report issued by The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation concluded that the number of same-sex couples in the U.S. grew from 2000 to 2005, from nearly 600,000 couples in 2000 to almost 777,000 in 2005. 4.1% of Americans aged 18–45 identify as gay, lesbian, or bisexual[51] (Other estimates have varied depending on methodology and timing; see Demographics of sexual orientation for a list of studies.) The American Community Survey from the 2000 U.S. Census estimated 776,943 same-sex couple households in the country as a whole, representing about 0.5% of the population.[51]
Less than 1% of Americans serve in the Armed Forces.[52]
Religion

The table below is based mainly on selected data as reported to the United States Census Bureau. It only includes the voluntary self-reported membership of religious bodies with 750,000 or more. The definition of a member is determined by each religious body.[53] As of 2004[update], the US census bureau reported that about 13% of the population did not identify itself as a member of any religion.[54]
| Religious body | Year reported | Places of worship reported | Membership (thousands) |
Number of clergy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| African Methodist Episcopal Church | 1999 | - | 2500 | 7741 |
| African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church | 2002 | 3226 | 1431 | 3252 |
| American Baptist Association | 1998 | 1760 | 275 | 1740 |
| Amish, Old Order | 1993 | 898 | 227 | 3592 |
| American Baptist Churches USA | 1998 | 3800 | 1507 | 4145 |
| Antiochian Orthodox Christian Archdiocese of North America | 1998 | 220 | 65 | 263 |
| Armenian Apostolic Church | 1998 | 28 | 200 | 25 |
| Assemblies of God | 1998 | 11937 | 2526 | 18148 |
| Baptist Bible Fellowship International | 1997 | 4500 | 1200 | - |
| Baptist General Conference | 1998 | 876 | 141 | - |
| Baptist Missionary Association of America | 1999 | 1334 | 235 | 1525 |
| Buddhism | 2001 | - | 1082 | - |
| Christian and Missionary Alliance, The | 1998 | 1964 | 346 | 1629 |
| Christian Brethren (Plymouth Brethren) | 1997 | 1150 | 100 | - |
| Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) | 1997 | 3818 | 879 | 3419 |
| Independent Christian Churches/Churches of Christ | 1998 | 5579 | 1072 | 5525 |
| Christian Congregation, Inc., The | 1998 | 1438 | 117 | 1436 |
| Christian Methodist Episcopal Church | 1983 | 2340 | 719 | - |
| Christian Reformed Church in North America | 1998 | 733 | 199 | 655 |
| Church of God in Christ | 1991 | 15300 | 5500 | 28988 |
| Church of God of Prophecy | 1997 | 1908 | 77 | 2000 |
| Church of God (Anderson, IN) | 1998 | 2353 | 234 | 3034 |
| Church of God (Cleveland, Tennessee) | 1995 | 6060 | 753 | 3121 |
| The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints | 2005 | 12753 | 5691 | 38259 |
| Church of the Brethren | 1997 | 1095 | 141 | 827 |
| Church of the Nazarene | 1998 | 5101 | 627 | 4598 |
| Churches of Christ | 1999 | 15000 | 1500 | 14500 |
| Conservative Baptist Association of America | 1998 | 1200 | 200 | - |
| Community of Christ | 1998 | 1236 | 140 | 19319 |
| Coptic Orthodox Church | 2003 | 200 | 1000 | 200 |
| Cumberland Presbyterian Church | 1998 | 774 | 87 | 634 |
| Episcopal Church | 1996 | 7390 | 2365 | 8131 |
| Evangelical Covenant Church, The | 1998 | 628 | 97 | 607 |
| Evangelical Free Church of America, The | 1995 | 1224 | 243 | 1936 |
| Evangelical Lutheran Church in America | 1998 | 10862 | 5178 | 9646 |
| Evangelical Presbyterian Church | 1998 | 187 | 61 | 262 |
| Free Methodist Church of North America | 1998 | 990 | 73 | - |
| Full Gospel Fellowship | 1999 | 896 | 275 | 2070 |
| General Association of General Baptists | 1997 | 790 | 72 | 1085 |
| General Association of Regular Baptist Churches | 1998 | 1415 | 102 | - |
| U.S. Conference of Mennonite Brethren Churches | 1996 | 368 | 82 | 590 |
| Grace Gospel Fellowship | 1992 | 128 | 60 | 160 |
| Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America | 1998 | 523 | 1955 | 596 |
| Hinduism | 2001 | - | 766 | - |
| Independent Fundamental Churches of America | 1999 | 659 | 62 | - |
| International Church of the Foursquare Gospel | 1998 | 1851 | 238 | 4900 |
| International Council of Community Churches | 1998 | 150 | 250 | 182 |
| International Pentecostal Holiness Church | 1998 | 1716 | 177 | 1507 |
| Islam | 2001 | - | 1104 | - |
| Jehovah's Witnesses | 2007 | 12494 | 1040 | - |
| Judaism | 2006 | 3727 | 6452 | - |
| Lutheran Church - Missouri Synod, The | 1998 | 6218 | 2594 | 5227 |
| Mennonite Church USA | 2005 | 943 | 114 | - |
| National Association of Congregational Christian Churches | 1998 | 416 | 67 | 534 |
| National Association of Free Will Baptists | 1998 | 2297 | 210 | 2800 |
| National Baptist Convention of America, Inc. | 1987 | 2500 | 3500 | 8000 |
| National Baptist Convention, USA, Inc. | 1992 | 33000 | 8200 | 32832 |
| National Missionary Baptist Convention of America | 1992 | - | 2500 | - |
| Orthodox Church in America | 1998 | 625 | 1000 | 700 |
| Pentecostal Assemblies of the World, Inc. | 1998 | 1750 | 1500 | 4500 |
| Pentecostal Church of God | 1998 | 1237 | 104 | - |
| Pentecostal Church International, United | 2008 | 28351 | 4037 | 22881 |
| Presbyterian Church in America | 1997 | 1340 | 280 | 1642 |
| Presbyterian Church (U.S.A.) | 1998 | 11260 | 3575 | 9390 |
| Progressive National Baptist Convention, Inc. | 1995 | 2000 | 2500 | - |
| Reformed Church in America | 1998 | 902 | 296 | 915 |
| Religious Society of Friends (Conservative) | 1994 | 1200 | 104 | - |
| Roman Catholic Church | 2002 | 19484 | 66404 | 50,017 (1997)[55] |
| Romanian Orthodox Episcopate | 1996 | 37 | 65 | 37 |
| Salvation Army, The | 1998 | 1388 | 471 | 2920 |
| Scientology | 2005 | 1300 | 55[56] | 1 |
| Serbian Orthodox Church | 1986 | 68 | 67 | 60 |
| Seventh-day Adventist Church | 1998 | 4405 | 840 | 2454 |
| Sikhism | 1999 | 244 | 80 | - |
| Southern Baptist Convention | 1998 | 40870 | 16500 | 71520 |
| Unitarian Universalism | 2001 | - | 629 | - |
| United Church of Christ | 1998 | 6017 | 1421 | 4317 |
| United House of Prayer For All People | - | 100 | 2500 | - |
| United Methodist Church, The | 1998 | 36170 | 8400 | - |
| Wesleyan Church, The | 1998 | 1590 | 120 | 1806 |
| Wisconsin Evangelical Lutheran Synod | 1997 | 1240 | 411 | 1222 |
| Religions of the United States | |||||||||
|
|||||||||
Religions of American adults
The United States government does not collect religious data in its census. The survey below, the American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) 2008, was a random digit-dialed telephone survey of 54,461 American residential households in the contiguous United States. The 1990 sample size was 113,723; 2001 sample size was 50,281
Adult respondents were asked the open-ended question, "What is your religion, if any?". Interviewers did not prompt or offer a suggested list of potential answers. The religion of the spouse or partner was also asked. If the initial answer was "Protestant" or "Christian" further questions were asked to probe which particular denomination. About one third of the sample was asked more detailed demographic questions.
Religious Self-Identification of the U.S. Adult Population: 1990, 2001, 2008[57]
Figures are not adjusted for refusals to reply; investigators suspect refusals are possibly more representative of "no religion" than any other group.
| Group |
1990 adults x 1,000 |
2001 adults x 1,000 |
2008 adults x 1,000 |
Numerical Change 1990- 2008 as % of 1990 |
1990 % of adults |
2001 % of adults |
2008 % of adults |
change in % of total adults 1990- 2008 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult population, total | 175,440 | 207,983 | 228,182 | 30.1% | ||||
| Adult population, Responded | 171,409 | 196,683 | 216,367 | 26.2% | 97.7% | 94.6% | 94.8% | -2.9% |
| Total Christian | 151,225 | 159,514 | 173,402 | 14.7% | 86.2% | 76.7% | 76.0% | -10.2% |
| Catholic | 46,004 | 50,873 | 57,199 | 24.3% | 26.2% | 24.5% | 25.1% | -1.2% |
| non-Catholic Christian | 105,221 | 108,641 | 116,203 | 10.4% | 60.0% | 52.2% | 50.9% | -9.0% |
| Baptist | 33,964 | 33,820 | 36,148 | 6.4% | 19.4% | 16.3% | 15.8% | -3.5% |
| Mainline Christian | 32,784 | 35,788 | 29,375 | -10.4% | 18.7% | 17.2% | 12.9% | -5.8% |
| Methodist | 14,174 | 14,039 | 11,366 | -19.8% | 8.1% | 6.8% | 5.0% | -3.1% |
| Lutheran | 9,110 | 9,580 | 8,674 | -4.8% | 5.2% | 4.6% | 3.8% | -1.4% |
| Presbyterian | 4,985 | 5,596 | 4,723 | -5.3% | 2.8% | 2.7% | 2.1% | -0.8% |
| Episcopalian/Anglican | 3,043 | 3,451 | 2,405 | -21.0% | 1.7% | 1.7% | 1.1% | -0.7% |
| United Church of Christ | 438 | 1,378 | 736 | 68.0% | 0.2% | 0.7% | 0.3% | 0.1% |
| Christian Generic | 25,980 | 22,546 | 32,441 | 24.9% | 14.8% | 10.8% | 14.2% | -0.6% |
| Christian Unspecified | 8,073 | 14,190 | 16,384 | 102.9% | 4.6% | 6.8% | 7.2% | 2.6% |
| Non-denominational Christian | 194 | 2,489 | 8,032 | 4040.2% | 0.1% | 1.2% | 3.5% | 3.4% |
| Protestant - Unspecified | 17,214 | 4,647 | 5,187 | -69.9% | 9.8% | 2.2% | 2.3% | -7.5% |
| Evangelical/Born Again | 546 | 1,088 | 2,154 | 294.5% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.9% | 0.6% |
| Pentecostal/Charismatic | 5,647 | 7,831 | 7,948 | 40.7% | 3.2% | 3.8% | 3.5% | 0.3% |
| Pentecostal - Unspecified | 3,116 | 4,407 | 5,416 | 73.8% | 1.8% | 2.1% | 2.4% | 0.6% |
| Assemblies of God | 617 | 1,105 | 810 | 31.3% | 0.4% | 0.5% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Church of God | 590 | 943 | 663 | 12.4% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 0.0% |
| Other Protestant Denominations | 4,630 | 5,949 | 7,131 | 54.0% | 2.6% | 2.9% | 3.1% | 0.5% |
| Churches of Christ | 1,769 | 2,593 | 1,921 | 8.6% | 1.0% | 1.2% | 0.8% | -0.2% |
| Jehovah's Witness | 1,381 | 1,331 | 1,914 | 38.6% | 0.8% | 0.6% | 0.8% | 0.1% |
| Seventh-Day Adventist | 668 | 724 | 938 | 40.4% | 0.4% | 0.3% | 0.4% | 0.0% |
| Mormon/Latter-Day Saints | 2,487 | 2,697 | 3,158 | 27.0% | 1.4% | 1.3% | 1.4% | 0.0% |
| Total non-Christian religions | 5,853 | 7,740 | 8,796 | 50.3% | 3.3% | 3.7% | 3.9% | 0.5% |
| Jewish | 3,137 | 2,837 | 2,680 | -14.6% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 1.2% | -0.6% |
| Eastern Religions | 687 | 2,020 | 1,961 | 185.4% | 0.4% | 1.0% | 0.9% | 0.5% |
| Buddhist | 404 | 1,082 | 1,189 | 194.3% | 0.2% | 0.5% | 0.5% | 0.3% |
| Muslim | 527 | 1,104 | 1,349 | 156.0% | 0.3% | 0.5% | 0.6% | 0.3% |
| New Religious Movements & Others | 1,296 | 1,770 | 2,804 | 116.4% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.2% | 0.5% |
| None/ No religion, total | 14,331 | 29,481 | 34,169 | 138.4% | 8.2% | 14.2% | 15.0% | 6.8% |
| Agnostic+Atheist | 1,186 | 1,893 | 3,606 | 204.0% | 0.7% | 0.9% | 1.6% | 0.9% |
| Did Not Know/ Refused to reply | 4,031 | 11,300 | 11,815 | 193.1% | 2.3% | 5.4% | 5.2% | 2.9% |
Marriage
In 2010, the median age for marriage for men was 27; for women, 26.[58]
Income
In 2006, the median household income in the United States was around $46,000. Household and personal income depends on variables such as race, number of income earners, educational attainment and marital status.
| Median income levels | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Households | Persons, age 25 or older with earnings | Household income by race | |||||||
| All households | Dual earner households |
Per household member |
Males | Females | Both sexes | Asian | White, non-hispanic |
Hispanic | Black |
| $46,326 | $67,348 | $23,535 | $39,403 | $26,507 | $32,140 | $57,518 | $48,977 | $34,241 | $30,134 |
| Median personal income by educational attainment | |||||||||
| Measure | Some High School | High school graduate | Some college | Associate's degree | Bachelor's degree or higher | Bachelor's degree | Master's degree | Professional degree | Doctorate degree |
| Persons, age 25+ w/ earnings | $20,321 | $26,505 | $31,054 | $35,009 | $49,303 | $43,143 | $52,390 | $82,473 | $70,853 |
| Male, age 25+ w/ earnings | $24,192 | $32,085 | $39,150 | $42,382 | $60,493 | $52,265 | $67,123 | $100,000 | $78,324 |
| Female, age 25+ w/ earnings | $15,073 | $21,117 | $25,185 | $29,510 | $40,483 | $36,532 | $45,730 | $66,055 | $54,666 |
| Persons, age 25+, employed full-time | $25,039 | $31,539 | $37,135 | $40,588 | $56,078 | $50,944 | $61,273 | $100,000 | $79,401 |
| Household | $22,718 | $36,835 | $45,854 | $51,970 | $73,446 | $68,728 | $78,541 | $100,000 | $96,830 |
| Household income distribution | |||||||||
| Bottom 10% | Bottom 20% | Bottom 25% | Middle 33% | Middle 20% | Top 25% | Top 20% | Top 5% | Top 1.5% | Top 1% |
| $0 to $10,500 | $0 to $18,500 | $0 to $22,500 | $30,000 to $62,500 | $35,000 to $55,000 | $77,500 and up | $92,000 and up | $167,000 and up | $250,000 and up | $350,000 and up |
| Source: US Census Bureau, 2006; income statistics for the year 2005 | |||||||||
Social class
Social classes in the United States lack distinct boundaries and may overlap. The following table provides a summary of currently prominent academic theories on the stratification of American society:
| Academic Class Models | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dennis Gilbert, 2002 | William Thompson & Joseph Hickey, 2005 | Leonard Beeghley, 2004 | |||
| Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics | Class | Typical characteristics |
| Capitalist class (1%) | Top-level executives, high-rung politicians, heirs. Ivy League education common. | Upper class 1% | Top-level executives, celebrities, heirs; income of $500,000+ common. Ivy league education common. | The super-rich (0.9%) | Multi-millionaires whose incomes commonly exceed $350,000; includes celebrities and powerful executives/politicians. Ivy League education common. |
| The Rich (5%) | Households with net worth of $1 million or more; largely in the form of home equity. Generally have college degrees. | ||||
| Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly educated (often with graduate degrees), most commonly salaried, professionals and middle management with large work autonomy | Upper middle class[1] (15%) | Highly educated (often with graduate degrees) professionals & managers with household incomes varying from the high 5-figure range to commonly above $100,000 | ||
| Middle class (plurality/ majority?; ca. 46%) |
College educated workers with incomes considerably above-average incomes and compensation; a man making $57,000 and a woman making $40,000 may be typical. | ||||
| Lower middle class (30%) | Semi-professionals and craftsmen with a roughly average standard of living. Most have some college education and are white collar. | Lower middle class (32%) | Semi-professionals and craftsman with some work autonomy; household incomes commonly range from $35,000 to $75,000. Typically, some college education. | ||
| Working class (30%) | Clerical and most blue collar workers whose work is highly routinized. Standard of living varies depending on number of income earners, but is commonly just adequate. High school education. | ||||
| Working class (32%) | Clerical, pink and blue collar workers with often low job security; common household incomes range from $16,000 to $30,000. High school education. | Working class (ca. 40% - 45%) |
Blue collar workers and those whose jobs are highly routinized with low economic security; a man making $40,000 and a woman making $26,000 may be typical. High school education. | ||
| Working poor (13%) | Service, low-rung clerical and some blue collar workers. High economic insecurity and risk of poverty. Some high school education. | ||||
| Lower class (ca. 14% - 20%) | Those who occupy poorly-paid positions or rely on government transfers. Some high school education. | ||||
| Underclass (12%) | Those with limited or no participation in the labor force. Reliant on government transfers. Some high school education. | The poor (ca. 12%) | Those living below the poverty line with limited to no participation in the labor force; a household income of $18,000 may be typical. Some high school education. | ||
- References: Gilbert, D. (2002) The American Class Structure: In An Age of Growing Inequality. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth; Thompson, W. & Hickey, J. (2005). Society in Focus. Boston, MA: Pearson, Allyn & Bacon; Beeghley, L. (2004). The Structure of Social Stratification in the United States. Boston, MA: Pearson, Allyn & Bacon.
- 1 The upper middle class may also be referred to as "Professional class" Ehrenreich, B. (1989). The Inner Life of the Middle Class. NY, NY: Harper-Colins.
Health
A nationwide study io 2010 indicated that 19.5% of teens, aged 12-19, have developed "slight" hearing loss. "Slight" was defined as an inability to hear at 16 to 24 decibels.[59]
Demographic statistics
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.[60]
Median age
- 36.7 years (2009 est.)
Age structure
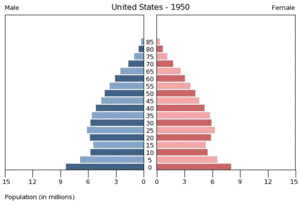
(2009 est.)
- 0–14 years: 20.2%
(male 31,639,127/female 30,305,704) - 15–64 years: 67.0%
(male 102,665,043/female 103,129,321) - 65 years and over: 12.8%
(male 16,901,232/female 22,571,696)
Population growth rate
- 0.977% (2009 est.)
Birth rate
- 13.5 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2009). This is the lowest in a century. There were 4,136,000 births.[61]
- 13.9 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2008)
- 14.3 births/1,000 population/year (Provisional Data for 2007)[62]
- In 2009, Time magazine reported that 40% of births were to unmarried women.[63]
- The drop in the birth rate from 2007 to 2009 is believed to be associated with the Great Recession[64]
Death rate
- 8.38 deaths/1,000 population/year (2009 est.)
Immigration
13% of the population was foreign-born in 2009.[65]
Net migration rate
- 4.32 migrants/1,000 population (2009 est.)
Sex ratios
(2009 est.)
- at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
- under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
- 15−64 years: 1 male(s)/female
- 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female
- total population: 0.97 male(s)/female
Infant mortality rate
(2009 est.)
- total population: 6.22 deaths/1,000 live births
- male: 6.9 deaths/1,000 live births
- female: 5.51 deaths/1,000 live births
Life expectancy at birth
(2009 est.)
- total population: 78.11 years
- male: 75.65 years
- female: 80.69 years
Total fertility rate
- 2.05 children born/woman (2009 est.)
Unemployment rate
(2008[66])
- All workers: 5.8%
- Adult men: 6.1%
- Adult women: 5.4%
- White: 5.2%
- Black or African American: 10.1%
- Hispanic or Latino ethnicity: 7.6%
- Asians: 4.0%
-
- (See also List of U.S. states by unemployment rate)
Nationality
- noun: American(s)
- adjective: American
Population projections
2008 US Census Bureau data[17]
- 2010: 310,232,863
- 2020: 341,386,665
- 2030: 373,503,674
- 2040: 405,655,295
- 2050: 439,010,253
See also
| Income in the United States |
|---|
|
|
Income by:
|
- U.S. demographic birth cohorts
- Maps of American ancestries
- Languages of the United States
- Immigration to the United States
- Emigration from the United States
- Places in the United States with notable demographic characteristics
- Demographic history of the United States
- Racial and ethnic demographics of the United States
- Historical Statistics of the United States
Lists:
- Lists of U.S. cities with non-white majority populations
- List of the largest metropolitan areas in the Americas
- List of U.S. states and territories by population
Income:
- Household income in the United States
- Personal income in the United States
- Affluence in the United States
- Highest-income places in the United States
- Lowest-income counties in the United States
References
- ↑ U.S. Population Clock. U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/main/www/popclock.html. This was the population today, at 00:00 UTC.
- ↑ "United Nations Population Division: World Urbanization Prospects; Table A.2 (p.81)" (PDF). United Nations. February 2008. http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/wup2007/2007WUP_Highlights_web.pdf. Retrieved 2008-05-03.
- ↑ "Table 13. State Population - Rank, Percent Change, and Population Density" (Excel). U.S. Census Bureau. 2007-12-27. http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/tables/09s0013.xls. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ "Mean Center of Population for the United States: 1790 to 2000" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/meanctr.pdf. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Total fertility rate". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2127rank.html. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook - Notes and Definitions". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/notesanddefs.html#2127. Retrieved 2010-02-01.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "CIA - The World Factbook -- Field Listing - Population growth rate". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2002.html. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- Rank Order - Net migration rate". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2112rank.html. Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ↑ "Monthly Population Estimates for the United States: April 1, 2000 to December 1, 2009 (NA-EST2009-01)". U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division. December, 2009. http://www.census.gov/popest/national/NA-EST2009-01.html. Retrieved 2010-01-06..
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "United States - Age and Sex". 2007 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/STTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=01000US&-qr_name=ACS_2007_1YR_G00_S0101&-ds_name=ACS_2007_1YR_G00_&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false&-state=st&-CONTEXT=st. Retrieved 2010-07-25.
- ↑ US Census Press Releases, U.S. Census Bureau
- ↑ "Statistical Abstract of the United States" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/prod/2005pubs/06statab/pop.pdf.
- ↑ "U.S. population hits 300 million mark". MSNBC (Associated Press). 2006-10-17. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/15298443/. Retrieved 2006-10-17.
- ↑ "Population Is Now One-Third Minority". http://www.prb.org/Articles/2006/IntheNewsUSPopulationIsNowOneThirdMinority.aspx?p=1U.S..
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau: Minority Population Tops 100 Million". Archived from the original on 2008-04-20. http://web.archive.org/web/20080420095712/http://www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/releases/archives/population/010048.html.
- ↑ http://pewhispanic.org/reports/report.php?ReportID=85
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 "Projected Population by Single Year of Age, Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: July 1, 2000 to July 1, 2050". U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/population/www/projections/downloadablefiles.html. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ↑ "World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision, Highlights, Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP.202; Table A.2" (PDF). United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2007). http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/wpp2006/WPP2006_Highlights_rev.pdf. Retrieved 2009-01-10.
- ↑ "Not Just Black and White: Historical and Contemporary Perspectives on Immigration, Race, and Ethnicity in the United States". Nancy Foner, George M. Fredrickson (2005). p.120. ISBN 0-87154-270-6
- ↑ "Immigrants in the United States and the Current Economic Crisis", Demetrios G. Papademetriou and Aaron Terrazas, Migration Policy Institute, April 2009.
- ↑ "Immigration Worldwide: Policies, Practices, and Trends". Uma A. Segal, Doreen Elliott, Nazneen S. Mayadas (2010). Oxford University Press US. p.32. ISBN 0-19-538813-5
- ↑ ""The First Measured Century: An Illustrated Guide to Trends in America, 1900–2000"". Public Broadcasting Service (PBS).
- ↑ "Changing Face of Western Cities". The Washington Post. August 21, 2006.
- ↑ "U.S. Nears Racial Milestone". The Wall Street Journal. June 11, 2010.
- ↑ "The 2008 Global Cities Index". Foreign Policy (November/December 2008). October 21, 2008. http://www.foreignpolicy.com/story/cms.php?story_id=4509. Retrieved 2009-01-30.
- ↑ "The World According to GaWC - Classification of cities 2008". 2008. http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/world2008t.html. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "The World According to GaWC - Cartogram of alpha cities 2008". 2008. http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/world2008c.html. Retrieved 2010-06-24.
- ↑ "Table 1: Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places Over 100,000, Ranked by July 1, 2008 Population: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008" (PDF). 2008 Population Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division. 2009-07-01. http://hawaii.gov/dbedt/info/census/popestimate/copy_of_2008-subcounty-population-hawaii/SUB_EST2008_01.pdf. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- ↑ "Table 5. Estimates of Population Change for Metropolitan Statistical Areas and Rankings: July 1, 2007 to July 1, 2008" (PDF). 2008 Population Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau. 2009-03-19. http://hawaii.gov/dbedt/info/census/popestimate/2008_MSA_Hawaii/CBSA_EST2008_05.pdf. Retrieved 2009-10-11.
- ↑ "Figure A–3. Census Regions, Census Divisions, and Their Constituent States". U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/tiger/glossry2.pdf. Retrieved 2007-06-17.
- ↑ "Somerville, MA (Massachusetts) Houses and Residents". city-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/housing/houses-Somerville-Massachusetts.html. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ↑ "Central Falls, Rhode Island". city-data.com. http://www.city-data.com/city/Central-Falls-Rhode-Island.html. Retrieved 2008-08-08.
- ↑ http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/06/0606000.html
- ↑ Census 2000 Population Distribution in the United States. U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/mapGallery/2kpopden.html. Retrieved 2007-12-14.
- ↑ Density Using Land Area For States, Counties, Metropolitan Areas, and Places. U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/population/www/censusdata/density.html. Retrieved 2007-12-14.
- ↑ "B02001. RACE - Universe: TOTAL POPULATION". 2008 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-context=dt&-ds_name=ACS_2008_1YR_G00_&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=ACS_2008_1YR_G2000_B02001&-tree_id=306&-redoLog=false&-all_geo_types=N&-currentselections=ACS_2006_EST_G2000_B02001&-geo_id=01000US&-search_results=01000US&-format=&-_lang=en. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 "B03002. HISPANIC OR LATINO ORIGIN BY RACE - Universe: TOTAL POPULATION". 2008 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates. United States Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-context=dt&-ds_name=ACS_2008_1YR_G00_&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=ACS_2008_1YR_G2000_B03002&-tree_id=306&-redoLog=false&-all_geo_types=N&-geo_id=01000US&-format=&-_lang=en. Retrieved 2009-12-08.
- ↑ "U.S. Census Bureau Guidance on the Presentation and Comparison of Race and Hispanic Origin Data". http://www.census.gov/population/www/socdemo/compraceho.html. Retrieved 2007-04-05. "Race and Hispanic origin are two separate concepts in the federal statistical system. People who are Hispanic may be of any race. People in each race group may be either Hispanic or Not Hispanic. Each person has two attributes, their race (or races) and whether or not they are Hispanic."
- ↑ "American FactFinder Help: Hispanic or Latino origin". U.S. Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/home/en/epss/glossary_h.html. Retrieved 2008-06-13.
- ↑ Projection data from U.S. Census Bureau
- ↑ White Americans no longer a majority by 2042
- ↑ U.S. to Grow Grayer, More Diverse
- ↑ Pew Research Center: Immigration to Play Lead Role In Future U.S. Growth
- ↑ U.S. Hispanic population to triple by 2050, USATODAY.com
- ↑ Study Sees Non-Hispanic Whites Shrinking to Minority Status in U.S. - February 12, 2008, The New York Sun
- ↑ Whites to become minority in U.S. by 2050, Reuters
- ↑ An Older and More Diverse Nation by Midcentury, U.S. Census Press Releases, 14 August 2008 (archived from the original on 2008-08-22)
- ↑ Kanell, Michael E. (16 November 2009). "Number of veterans, October". Atlanta, Georgia: Atlanta Constitution-Journal. pp. A6. http://www.ajc.com/business/vets-jobs-challenges-in-199084.html. quoting the Bureau of Labor Statistics
- ↑ Hsu, Spencer S. (2 May 2010). "Immigration plan shows a shift to the right". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. A3.
- ↑ "2000 Census information on Gay and Lesbian Couples". gaydemographics.org. http://www.gaydemographics.org/USA/USA.htm.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Gary J. Gates Same-sex Couples and the Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual Population: New Estimates from the American Community SurveyPDF (2.07 MiB). The Williams Institute on Sexual Orientation Law and Public Policy, UCLA School of Law October, 2006. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ↑ Davenport, Christian (20 April 2010). "A disconnect at Magruder". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. B1. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/04/19/AR2010041903879.html?nav=emailpage.
- ↑ Table No. 68. Religious Bodies—Selected Data (p. 59), "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005 (tables 67-69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/04statab/pop.pdf.
- ↑ "Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005 (tables 67-69)" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/04statab/pop.pdf.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ "Section 1. Population". Statistical Abstract of the United States: 2004-2005. U.S. Census Bureau. p. 55. http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/04statab/pop.pdf. Retrieved 2008-06-29. (Table No. 67. Self-described religious identification of adult population: 1990 and 2001; data for 2001).
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 Barry A. Kosmin and Ariela Keysar (2009). "AMERICAN RELIGIOUS IDENTIFICATION SURVEY (ARIS) 2008" (PDF). Hartford, Connecticut, USA: Trinity College. http://b27.cc.trincoll.edu/weblogs/AmericanReligionSurvey-ARIS/reports/ARIS_Report_2008.pdf. Retrieved 2009-04-01.
- ↑ Riley, Naomi Schaefer (6 June 2010). "Love conquers all. Except religion". Washington, DC: Washington Post. pp. B1, B4. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/06/04/AR2010060402011.html.
- ↑ Johnson, Carla K. (18 August 2010). "1 in 5 teens has some hearing loss". Burlington, Vermont: Burlington Free Press. pp. 4A. http://www.whbf.com/Global/story.asp?S=12997646.
- ↑ "CIA - The World Factbook -- United States". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/us.html. Retrieved 2010-02-16.
- ↑ Marchione, Marilynn (28 August 2010). "Recession may have pushed U.S. birth rate to a new low". Burlington, Vermont: Burlington Free Press. pp. 3A. http://content.usatoday.net/dist/custom/gci/InsidePage.aspx?cId=burlingtonfreepress&sParam=34384945.story.
- ↑ Births, Marriages, Divorces, and Deaths: Provisional Data for 2009 National Vital Statistics Report Volume 58, Number 25, accessed August 28, 2010
- ↑ Amy Sullivan (March 20, 2009). "Behind the Boom in Adult Single Motherhood". http://www.time.com/time/nation/article/0,8599,1886814,00.html.
- ↑ "Birthrate Is Lowest in a Century" Associated Press article printed in The New York Times August 27, 2010, accessed August 28, 2010
- ↑ Starr, Tena (28 April 2010). "Mexican farmworker's life like living in a "golden cage"". Barton, Vermont: the Chronicle. pp. 12.
- ↑ Labor Force Characteristics by Race and Ethnicity, 2008, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (2008), Retrieved on 2010-04-24.
External links
- 2000 Census of Population and Housing United States, U.S. Census Bureau
- U.S. Demographics and State Rankings
- Asian-Nation: Demographics of Asian American /2006-07-04-us-population_x.htm?csp=34 Countdown to 300 million
- Census Ancestry Map
- USA Today 2004 Election County by County Map
- BeliefNet State by State Religious Affiliation (archived from the original on 2008-04-21)
- Health by State
- U.S. Demographics and Maps
- America's Changing Demographics a Nightly Business Report special
- The Realignment of America - The Wall Street Journal
- Religion U.S. Census Bureau
- Google - public data "Population in the U.S."
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||


